Artificial Intelligence (AI) is a top news story for consumers and businesses alike. Generative Pre-Trained (GPT) models and Large Language Models (LLM) such as Microsoft’s ChatGPT and Google’s Bard lead the pack of impressive publicly available software services that have rapidly changed the face of search and recommendations in the digital sphere. They generate text, translate languages, write creative content, and answer questions in a convincing way.
We have come a long way in 30 years! One of the first and most popular consumer websites was born in 1993: https://www.allrecipes.com/, where consumers could search, share, and later rate recipes online. Today, LLMs are changing the game. Rather than finding and searching through a vast and neatly organized list of recipes, then assembling what you need.
Consider trying something as simple as this on https://bard.google.com/u/1/: “I’m having a Thanksgiving Day meal with family and friends. What is a reasonably priced, delicious, and unique meal I can serve for eight people? List out the ingredients, the amounts, and instructions I should follow with eight people in mind.”
The benefits are clear.
Business benefits of LLMs
Increased efficiency: LLMs can be used to increase the efficiency of AI systems by automating tasks that would otherwise be time-consuming and labor-intensive. This can free up resources that can be used to focus on other aspects of privacy compliance.
Enhanced creativity: LLMs can be used to stay on top of privacy issues across various regulatory regimes, generate ideas, and help communicate concepts around privacy that would be traditionally laborious. Generally, in the hands of a domain expert that can readily spot truthful and helpful up to date information, AI can assist compliance with privacy regulations.
Generally, AI promises increased efficiency and enhanced creativity. Nonetheless, there are considerable risks associated with using LLMs in AI, including risks to privacy. Our 2023 TrustArc Privacy Benchmarks Survey results revealed that among 18 potential challenges, “artificial intelligence implications in privacy” ranked #1.
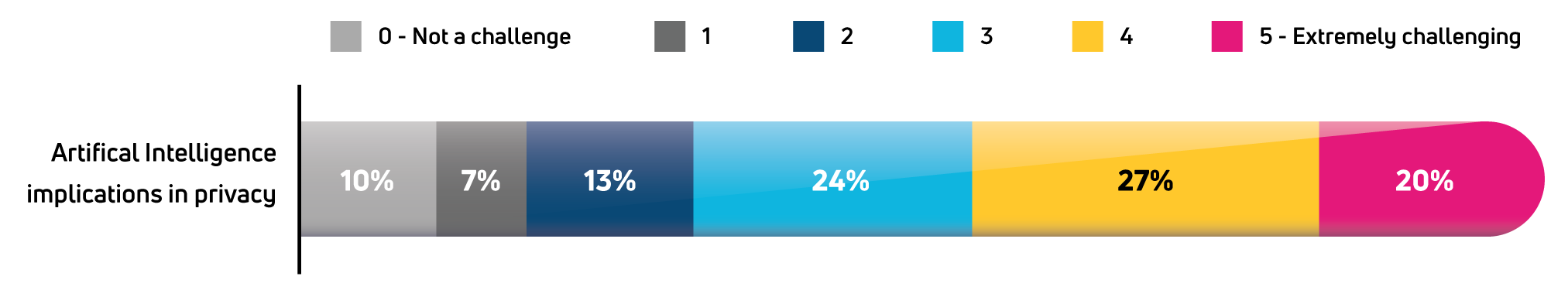
So why are privacy professionals worried about AI?
Data protection and security risks of LLMs
Data privacy: LLMs can be used to collect and process large amounts of personal data, to correlate among disparate systems, and to index and track individuals. While targeting with relevant advertising may be laudable from a business perspective, it also leaves wide open the possibilities for intentional or unintentional privacy breaches that consumers have not consented to.
Model bias and discrimination: LLMs are trained on large datasets of text and code. These datasets can contain biases, which can be reflected in the output of LLMs. This could lead to LLMs making discriminatory decisions, such as denying loans or jobs to certain groups of people.
Security: LLMs are complex systems that are vulnerable to security attacks. If an LLM is hacked, the attacker could gain access to the personal data that it has been trained on. This data could then be used to commit identity theft, fraud, or other crimes, including the unauthorized disclosure of personal data.
Data poisoning: An attacker could intentionally introduce malicious data into an AI model, which could cause the model to make incorrect and/or harmful decisions.
Model explainability: When it is difficult to understand how an AI model makes its decisions, it can be difficult to ensure that the model is making a fair and accurate representation of facts.
Incorrect or false results: LLMs regularly generate incorrect or false results, as their actual output is a probabilistic display of information that is programmed to read convincingly. Outputs include regular “hallucinations,” including fabricating false insights, as well as not necessarily having the most recent or up-to-date data.
To learn about mitigating the risks of using AI, read: Embracing the AI Revolution Responsibly: Elevating Privacy Impact Assessments (PIAs) to AI Governance.
Recent developments in proposed AI regulations
To counter these concerns, new AI related legislations are rapidly being drawn up.
The EU AI Act establishes a framework for the development and use of AI systems in the European Union. The regulation would include provisions on privacy and cybersecurity, such as requirements for data protection impact assessments and risk management.
The UK AI Act is a proposed law that would regulate the development and use of AI systems in the United Kingdom. The law would include provisions on privacy and cybersecurity, such as requirements for transparency and accountability.
The Canada Artificial Intelligence and Data Act (AIDA) is a proposed law that would regulate the development and use of AI systems in Canada. The law would include provisions on privacy and cybersecurity, such as requirements for consent and data protection.
The NIST AI Risk Management Framework is a set of guidelines developed by the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) that can be used to help organizations manage the risks associated with AI systems. The framework includes guidance on privacy and cybersecurity, such as requirements for data protection and risk assessment.






